
البحـث الأول
مجلة النفط والتعاون العربي
161
العدد
- 2017
أربعون
المجلد الثالث و ال
2016
أوابك العلمية لعام
�
ص لبحوث العلمية الفائزة بجائزة
�
عدد خا
35
25
-
Oil is hygroscopic, meaning that it absorbs moisture easily.
Burning fuel
produces CO
2
and H
2
O. When an engine is cold, the water generated can
pass through to the lube oil.
-
Oil picks up normal wear particles and debris as it circulates in the machine
or engine. It is usually trapped by the filter except when it is very small.
-
Dirt is carried by the air flowing into the reservoir and settles there.
-
Unburnt petrol/diesel passes through to the lube oil during engine start-ups
and contaminates lube oil.
-
Carbon forms as a result of incomplete combustion when an engine is
warming up and passes through to the lube oil.
-
Some contaminants, such as chlorinated solvents, are picked up by waste
oil during use or during storage while waiting for collection. However,
some little amounts may come from additives in the original product.
-
Deterioration of the additives where most contain complex chemicals
necessary for the performance of the oil.
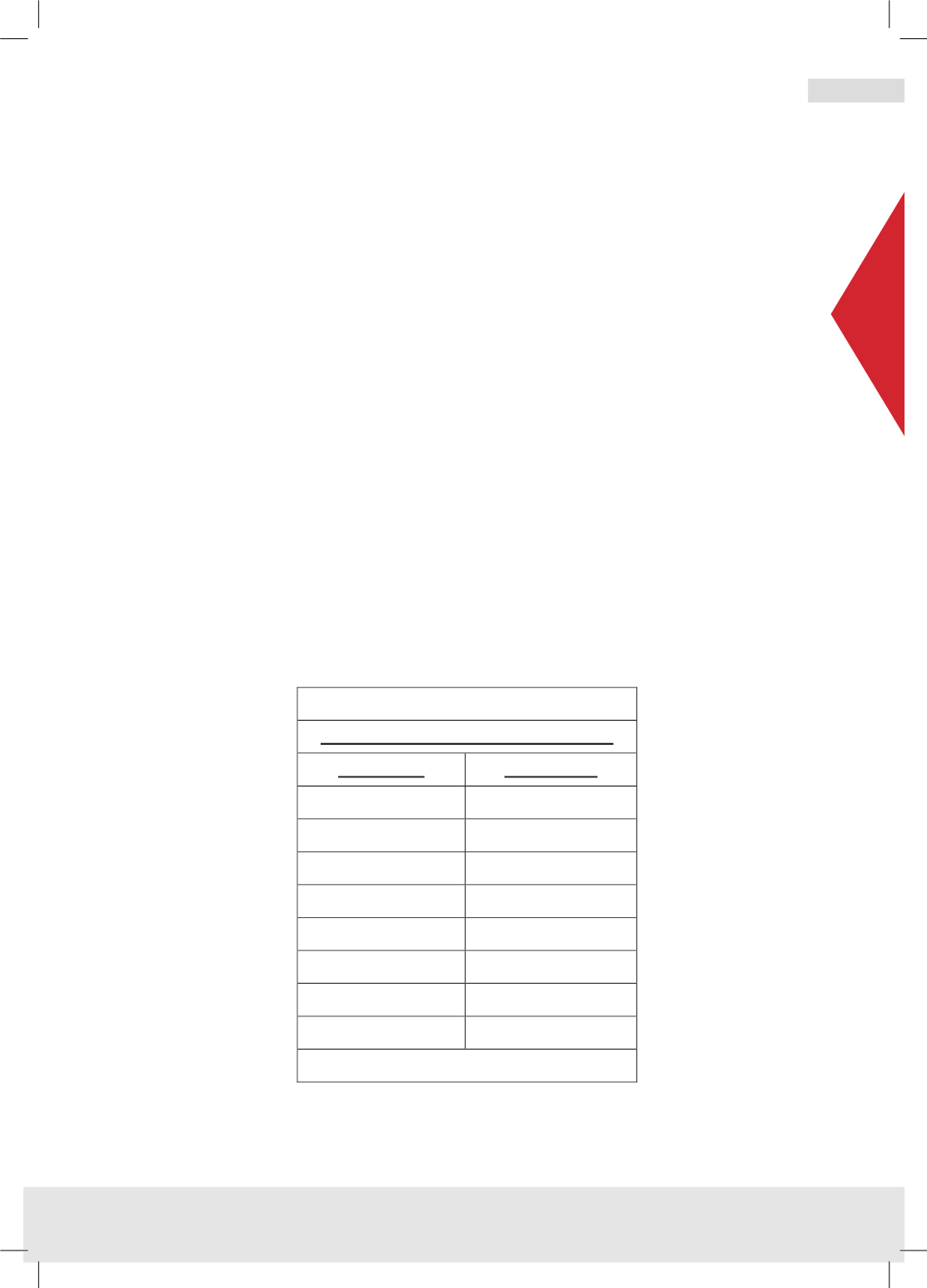
Table (3)
Typical Composition of Lubricating Oil
Component
% by weight
Base oil
71.5
–
96.2
Metallic detergents
2.0
–
10.2
Dispersant
1.0
–
9.0
Zinc dithiophosphate
0.5
–
3.0
Antioxidant/antiwear
0.1
–
2.0
Friction modifier
0.1
–
3.0
Pour point depressant
0.1
–
1.5
Antifoam
2
–
15 ppm
Source: 1 based on Lubrizol.
The combination of water, heat and oxygen enhances the deterioration and breaks
up both additive and base oil.
In the presence of oxygen, t
he
oxidation products
















